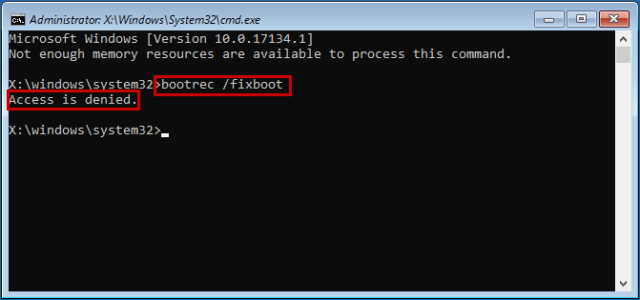
The “Bootrec /Fixboot access is denied” error can show up in the Windows Recovery Environment while executing the /fixboot command in order to boot up your computer.
This error can occur due to:
- Broken EFI structure
- Master Boot Record (MBR) failure
- Corrupt Windows or BCD file
- Windows 10 versions 1707 and 1709
This can be a big hassle for users because it prevents them from accessing valuable files, programs, and data when the system does not start.
Fortunately, several actions can be taken to resolve the bootrec /fixboot problem and restart the computer. These steps may include using the built-in Windows Startup Repair tool, reconfiguring boot files, executing the CHKDSK command, and more.
Regardless of your level of technical expertise, our instructions will enable you to quickly fix the bootrec /fixboot problem and restore your computer to full functionality.
What is The Bootrec /Fixboot Command?
Bootrec /fixboot is a command line to repair a Windows operating system’s boot sector. The boot sector is an essential component of the operating system since it contains the bootloader and other information required to start the computer.
If the boot sector is damaged or corrupted, the computer won’t start properly, resulting in a black screen.
How to Fix the Bootrec /Fixboot Access is Denied Error on Windows?
You can start off by doing the startup repair and if that doesn’t work, move on to the next methods. There’s no need to dive into complicated solutions before trying the easier ones.
Having said that, let’s take a look at all the fixes for Bootrec /Fixboot errors on Windows.
1. Perform Startup Repair from WinRE
You can perform the startup repair either with the installation media or without it. If you don’t have installation media already, then simply follow the steps below and you’ll be good to go.
- Shut down your system and restart it.
- While it is starting, you need to keep pressing the F11 key. This will take you to the Windows Recovery Environment.
Note: If pressing F11 doesn’t work, then try F9 or F8. Some systems would even require you to press and hold the Fn key.
- From WinRE, go to Troubleshoot.
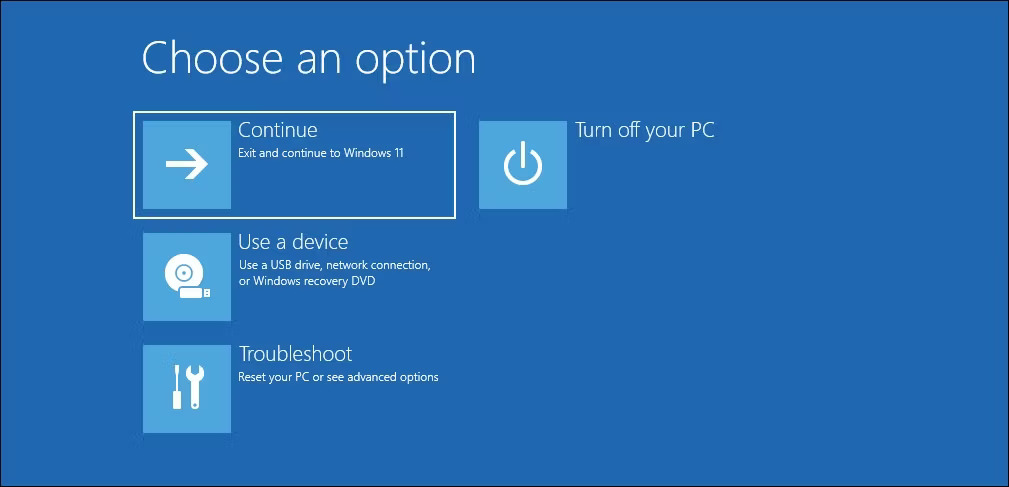
- Next, select Advanced Options.
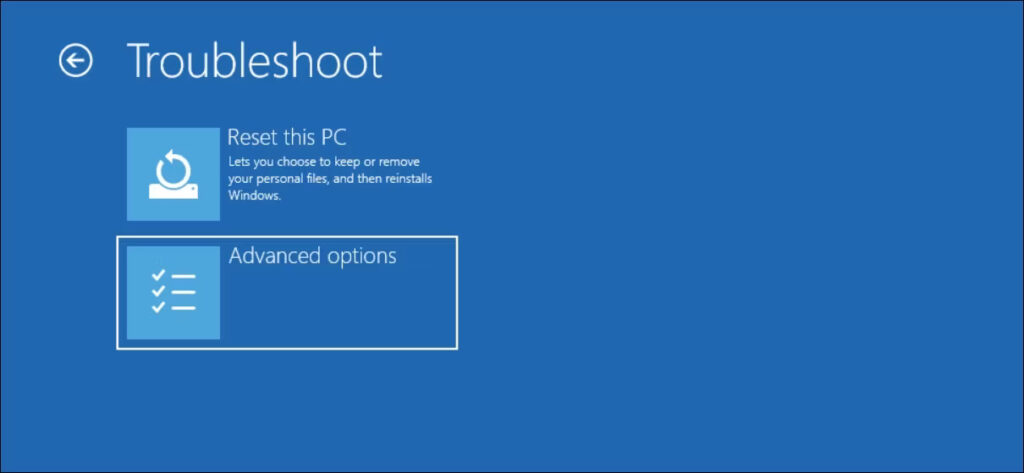
- Click on Startup Repair.
- Now click on your local user account and enter the password to proceed.
Note: In case you don’t have a password, just leave the blank space as it is.
Now you need to wait as Windows starts diagnosing your PC to look for potential problems. If it detects any issue, then simply move on with the on-screen instructions and the computer will boot up soon.
2. Reconfigure Boot Files After Recreating EFI Structure
The first method works most of the time. But just in case it doesn’t, recreate your EFI structure and reconfigure boot files to try and fix the bootrec /fixboot access is denied error.
The procedure is as follows:
- Shut down, and then start up your system.
- While it starts, press the F11, F9, or F8 keys to access Windows RE.
- Select Advanced Options in the Automatic Repair screen.
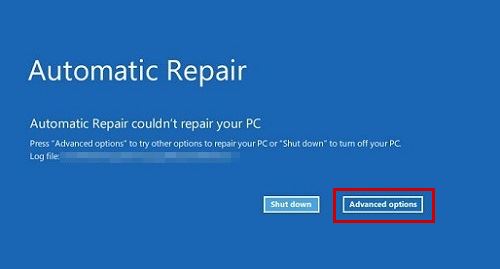
- Afterward, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options and select Command Prompt.
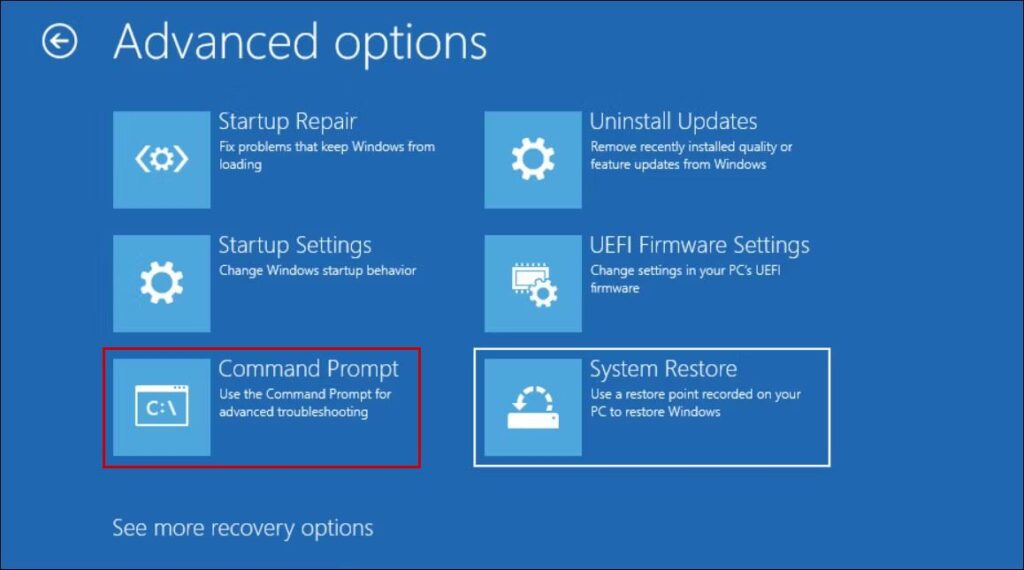
- To access the diskpart utility, type in the following command and hit Enter:
diskpart
- To get the complete list of disks on your computer, press Enter after typing:
list disk
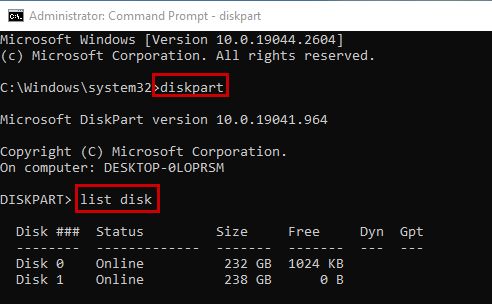
- Now execute the command:
select disk disk.
Note: Replace the disk at the end with the disk number on which your Windows is installed. For instance, if it’s on disk 1, then the command will become “select disk 1”. Make sure you select the disk number according to your system.
- Next, write the following command for listing all the volumes in the disk:
list vol
- Now select the partition with EFI. It will have FAT32 in the Fs section.
- Assuming it is Volume 5, type in the following command to choose the EFI partition volume:
select vol 5
Note: Make sure you select the volume according to your PC.
- Next, assign a letter to the selected volume that has not been assigned to any other one.
- Let’s assume you want to assign the letter A, then type in:
assign letter:A
- Now exit diskpart by writing:
exit
- Select the volume you just assigned the letter to by writing:
A:
Note: Replace A in the command above with the letter you assigned.
- Now in the EFI partition of the V Volume, you need to copy boot files with the following command:
bcdboot C:\windows /s V: /f UEFI
- Type exit to leave the command prompt after execution.
- Return to the Windows Recovery Menu and select Continue.
- Wait while the system restarts.
- Now try executing the bootrec /fixboot command to see if it works.
3. Run the CHKDSK Command
The CHKDSK command checks if there is an issue with any of the disks and then fixes it automatically. You need to run this command on the disk where Windows is installed.
Here’s how to execute this command:
- Enter the Windows Recovery Environment and go to Troubleshoot.
- Now select Advanced Options > Command Prompt.
- Considering your home drive is C, hit Enter after you write the following command:
chkdsk c: /r
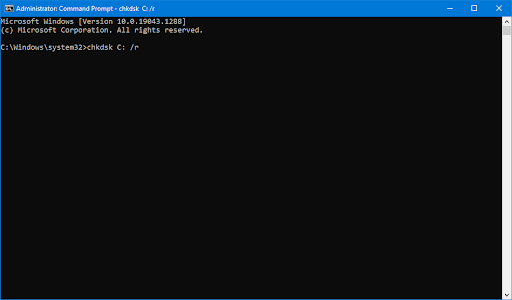
Note: If your Windows drive is not C but D or E maybe, then type chkdsk d: /r or chkdsk e: /r.
Now wait for the scan to complete and look for any errors in the disk.
4. Execute the Rebuild BCD Command
Executing the rebuildbcd command is another way to counter the “bootrec /fixboot access is denied” error.
The Boot Configuration Data (BCD) store can get corrupted or go missing. The boot manager needs the BCD store to load up the computer. So if it isn’t found or has errors, the system won’t start.
What the rebuildbcd command does is that it simply recreates or repairs the BCD store and boots up the PC.
Follow the steps below to execute it.
- Enter Windows Recovery Environment and head over to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Command Prompt.
- Press Enter after writing each of the following commands in order:
bootrec /rebuildbcd
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
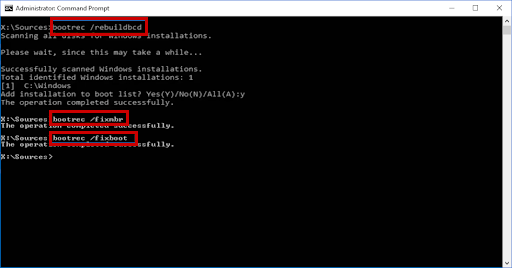
Wait for the execution to complete before attempting the bootrec /fixboot command to see if it works.
5. Turn off Fast Boot in BIOS.
Fast boot, as evident by the name, is a setting in BIOS that reduces the time it takes for a computer to boot up by skipping certain power-on self-tests (POSTs) and other startup processes. However, it can also become a reason for the bootrec /fixboot access denied error.
You need to disable Fast Boot as well as Secure Boot to try and fix the issue. This worked for many users and will do the same for you too.
Here’s how to do it:
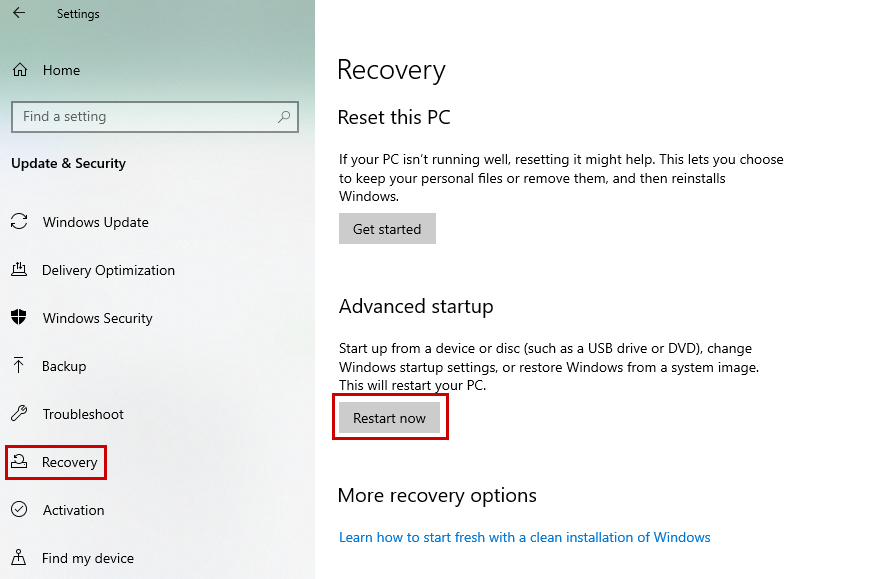
- From your PC, navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Recovery.
- Click on Restart Now from the Advanced Startup section on the right side.
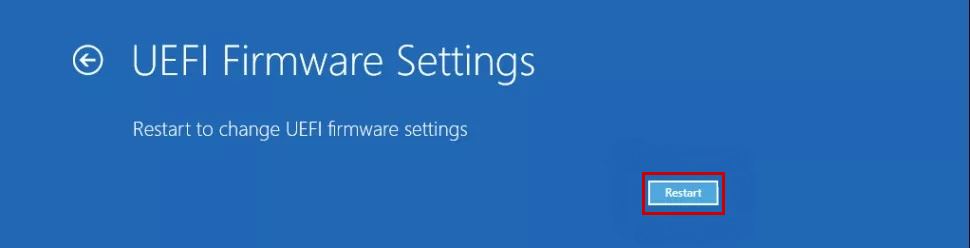
- Now navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > UEFI Firmware Settings.

Note: If there’s no option for UEFI Firmware Settings, then select Startup Settings and press F1 or F2 while your PC restarts to go into the BIOS menu.
- Click Restart.
- Now you’ll be on the BIOS menu.
- Disable the Fast Boot option under the Boot tab.
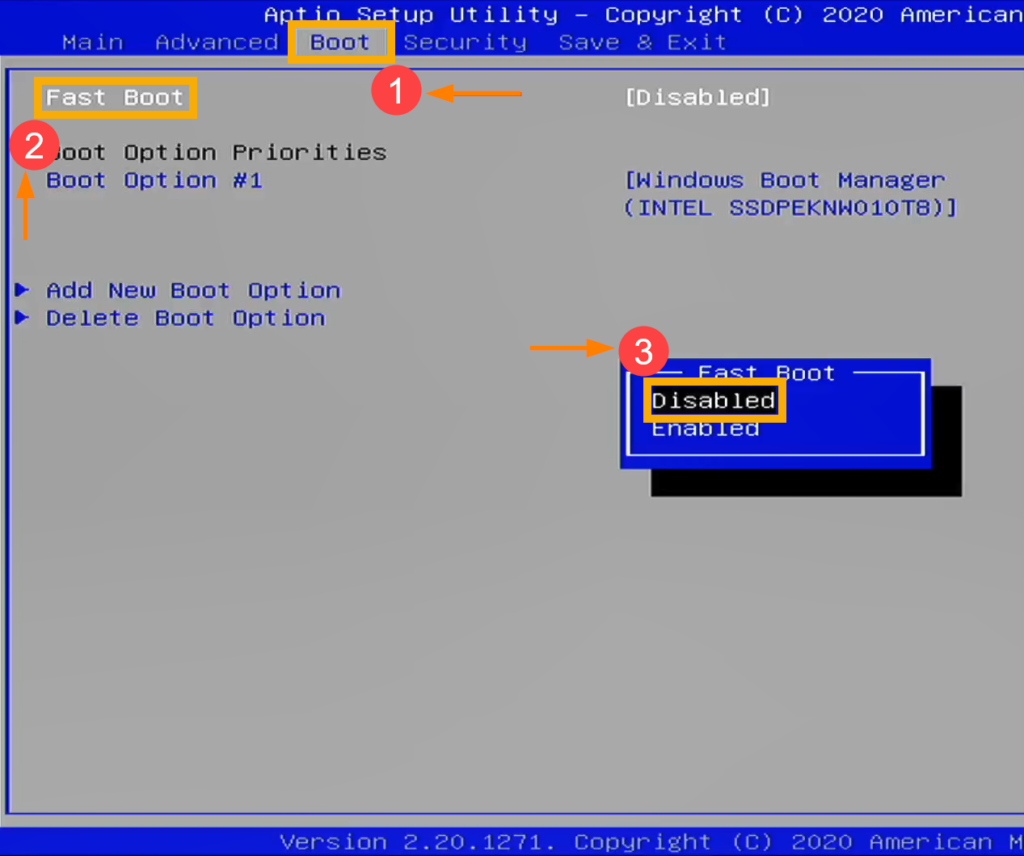
- Now go to the Security Tab and disable the Secure Boot option from there.
- Now select Exit Saving Changes before exiting.
- Restart your PC and see if the issue is resolved or not.
6. Backup your Data and Reinstall Windows
Finally, if none of the above methods work, you can try this one. It’s a simple Windows reinstallation; however, make sure you save all of your important files before carrying out the process.
You can use free tools like AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard and Recoverit to backup and then recover your data, or go for premium options such as MiniTool Partition Wizard Pro or EaseUS Data Recovery.
Read more: Why is my iPhone Battery Draining so Fast? (Fix it Now!)